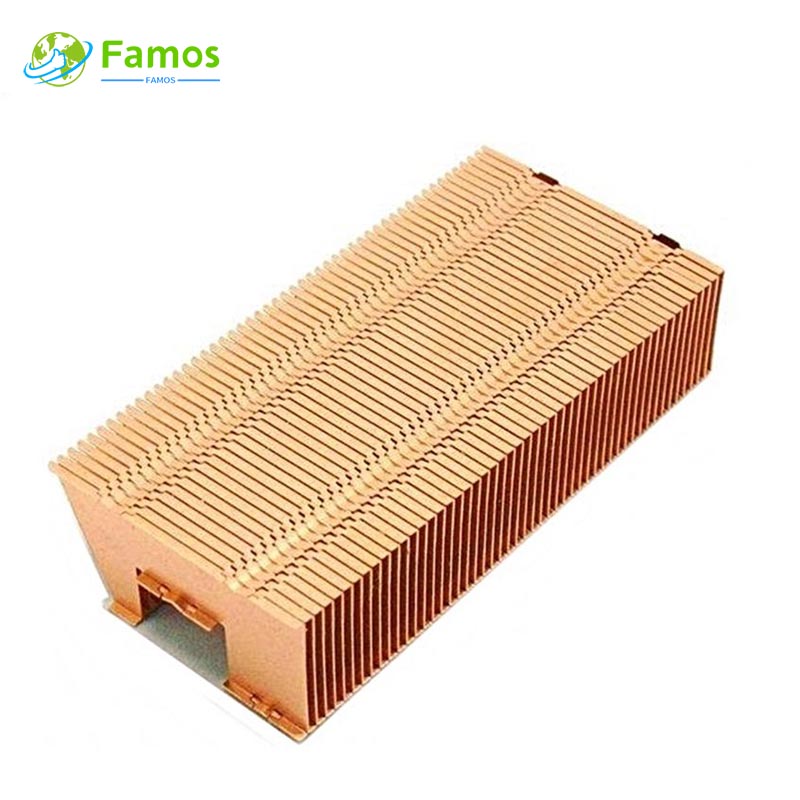
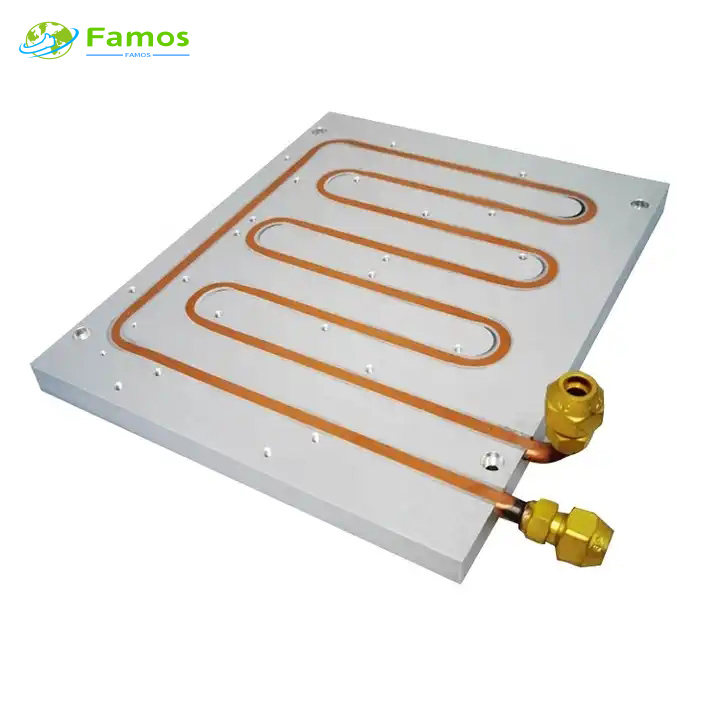
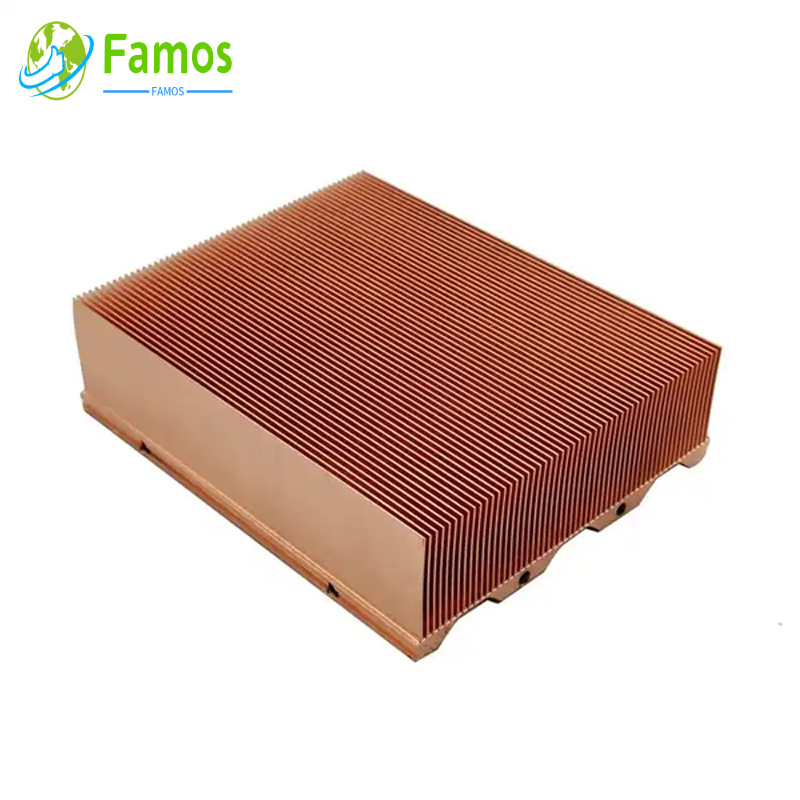
Before understanding how to select a heat sink, we need to know some knowledge about heat sinks
Heat sink Introduction
Heat sink is a heat dissipation material used in electronic equipment. It can effectively dissipate the heat generated inside the equipment to the outside, preventing electronic equipment from overheating and causing failure. Heat sinks are often used in high-temperature components such as CPUs, graphics cards, hard drives, and motherboards to maintain their stability and life.
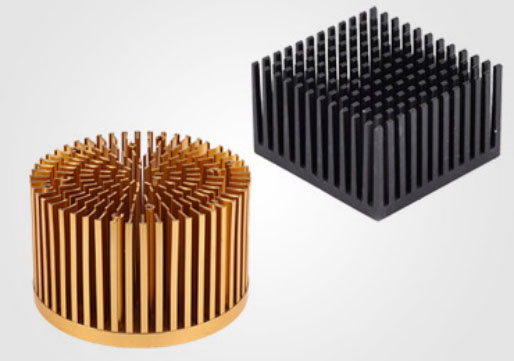
The material of the heat sink is usually a metal material with good thermal conductivity, such as aluminum, copper, magnesium, or non-metallic materials such as ceramics and glass fibers. Its function is similar to that of a car or computer radiator. During operation, the heat generated is conducted to the outer surface of the radiator for cooling. At the same time, the shape and structure of the heat sink are also important parameters that affect its heat dissipation efficiency. Common shapes include vertical, horizontal, spiral, sheet and other structures.
Heat sinks are often one of the first things to check when an electronic device starts to overheat. Choosing the right heat sink has a crucial impact on the service life and performance stability of the device. If the heat dissipation is insufficient and the heat cannot be dissipated in time, it may cause problems such as equipment performance degradation, card change, or even burning. Therefore, understanding the basic knowledge of heat sinks and choosing a suitable heat sink is also a key point in the maintenance and management of electronic equipment.
Heat sink types:
Different devices require different types of heat sinks. Below are some common types of heat sinks:
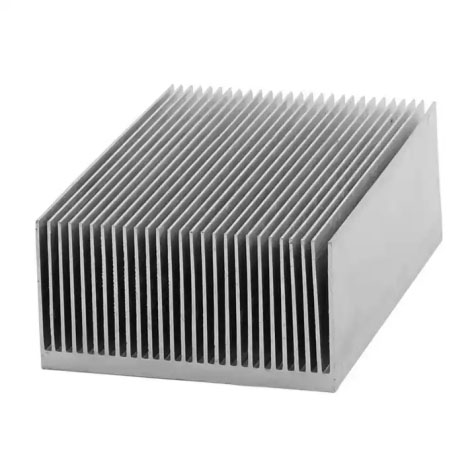
1. Aluminum heat sink
Aluminum heat sink is a common type of heat sink suitable for hardware devices such as CPUs and graphics cards. The aluminum heat sink has a simple process, low cost, and relatively low power limitation.

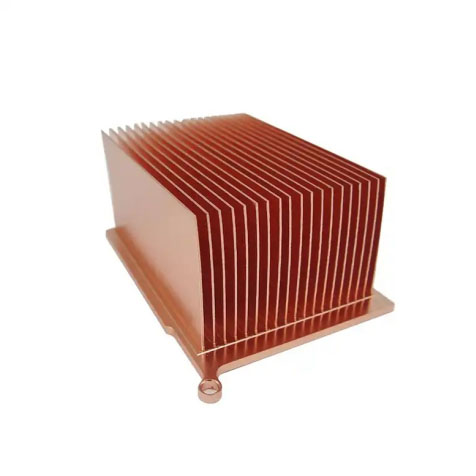
2. Copper heat sink
Copper heat sink has better heat dissipation effect than aluminum heat sink, but the cost is also higher. Copper heat sink is suitable for higher power devices, such as high-end desktop computers and some gaming laptops.

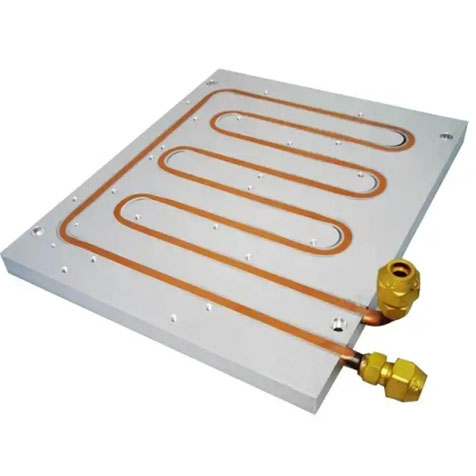
3. Water cooling heat sink
Water cooling heat sink is a way of using water to dissipate heat. This scheme uses water pipes to transfer heat to a separate heat sink, which then dissipates the heat. The water cooling solution is suitable for application scenarios such as desktops and servers.

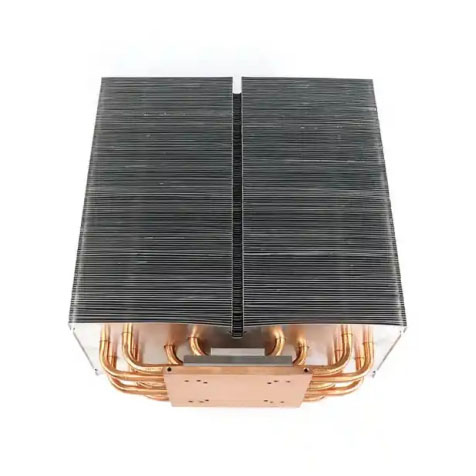
4.Heat pipe heat sink
The heat pipe heat sink uses heat pipe technology. A heat pipe is a heat transfer device that can quickly transfer heat to a heat sink to improve heat dissipation. Heat pipe heat sinks are commonly used in game consoles and high-performance computers.
The above are some common types of heat sinks. Choosing the appropriate heat sink based on different hardware devices and usage environments can better protect the stability and service life of hardware devices.

How to select a heat sink?
Heat sink is a commonly used heat sink material in electronic components, equipment, and products. It can enhance the heat dissipation performance of components and equipment, avoiding performance degradation or burning failures caused by overheating. The correct selection of heat sinks can provide a good guarantee for the service life and performance of electronic products. Below is an introduction of how to choose heat sinks.
1. Material selection
The material of the heat sink affects its heat dissipation performance. Usually, heat sinks mainly use metal materials such as aluminum, copper, magnesium, zinc, or non-metallic materials such as ceramics and glass fibers. The common aluminum heat sink is relatively cheap, but the heat dissipation effect is also relatively poor; The copper heat sink has excellent heat dissipation effect and high stability, but the price is also relatively high. Therefore, the selection of materials should be based on actual usage needs and whether funding is allowed for decision-making.
2. Size and structure of heat sinks
The size and structure of the heat sink are directly related to its heat dissipation performance. Usually, choosing a larger size and surface area heat sink has a better effect. In addition, the structure of the heat sink also affects its heat dissipation efficiency. The structure of heat sinks has different forms, including vertical, horizontal, spiral, and sheet structures. Therefore, when selecting heat sinks, the size and structure of the heat sinks should be selected based on actual needs to improve heat dissipation efficiency.
3. Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity refers to the heat dissipation capacity of a heat sink, usually expressed in W/(m * K). The higher the thermal conductivity, the higher the heat dissipation efficiency of the heat sink. Generally speaking, copper, as the basic material for heat dissipation fins, has high thermal conductivity. For example, the thermal conductivity of copper is about 400 W/(m * K), while the thermal conductivity of aluminum is about 240 W/(m * K). Therefore, when selecting heat sinks, priority should be given to thermal conductivity.
4. Installation method
The installation method of the heat sink also has a direct impact on the heat dissipation efficiency. In practical use, common installation methods for heat sinks include patch type, screw fixed type, buckle type, etc. Generally speaking, the larger the contact area between the heat sink and the cooled component, the higher the heat transfer efficiency. Therefore, when selecting heat sinks, appropriate installation methods should be selected based on actual needs.
In summary, when selecting a heat sink, multiple factors such as material, size and structure, thermal conductivity, and installation method should be considered. Choosing the appropriate heat sink can fully utilize the performance of components and equipment, improve their service life and stability.
Types of Heat Sink
In order to meet different heat dissipation requirements, our factory can produce different type heat sinks with many different process, such as below:
Post time: Apr-21-2023