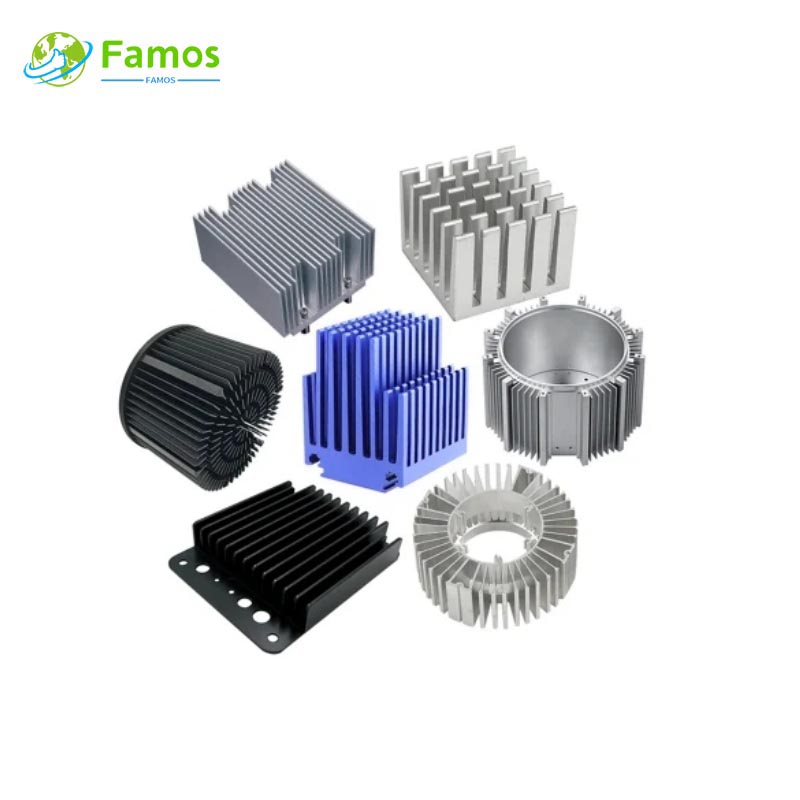
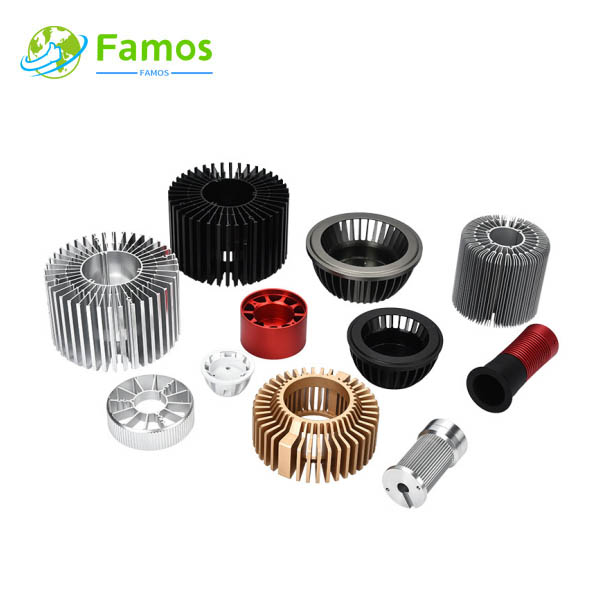
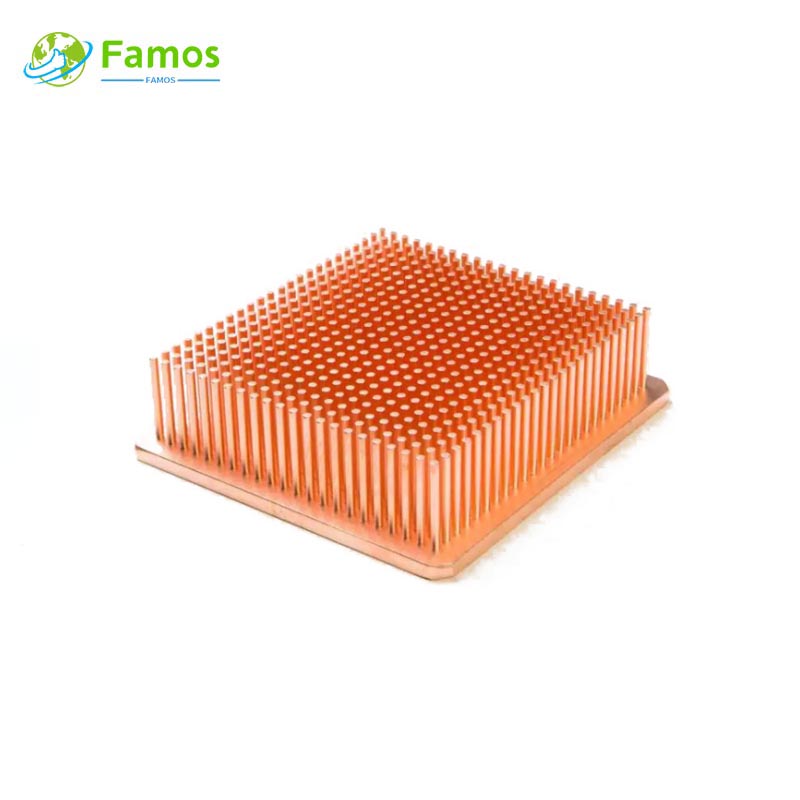
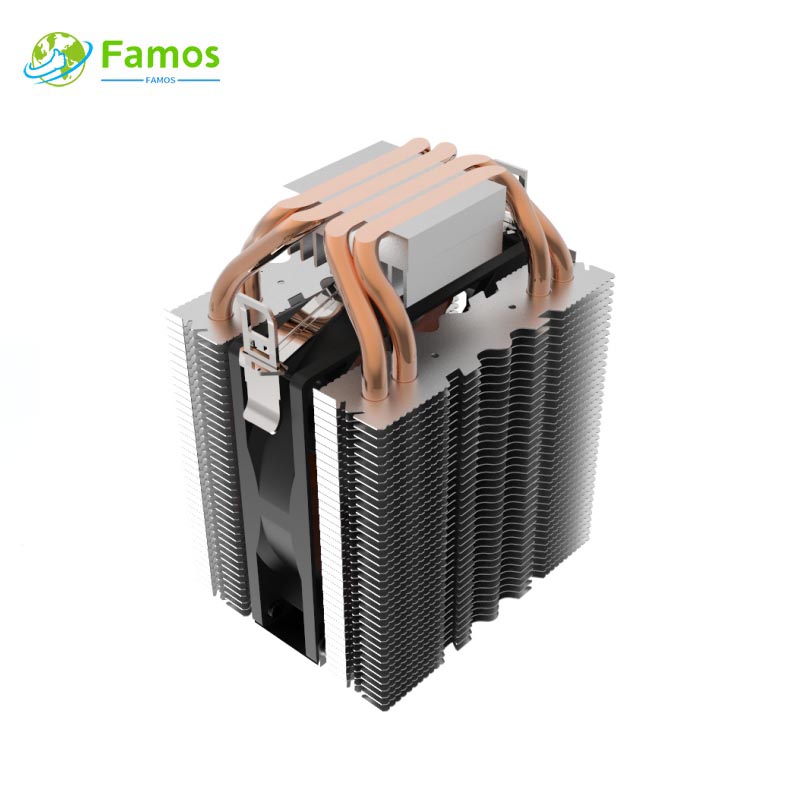
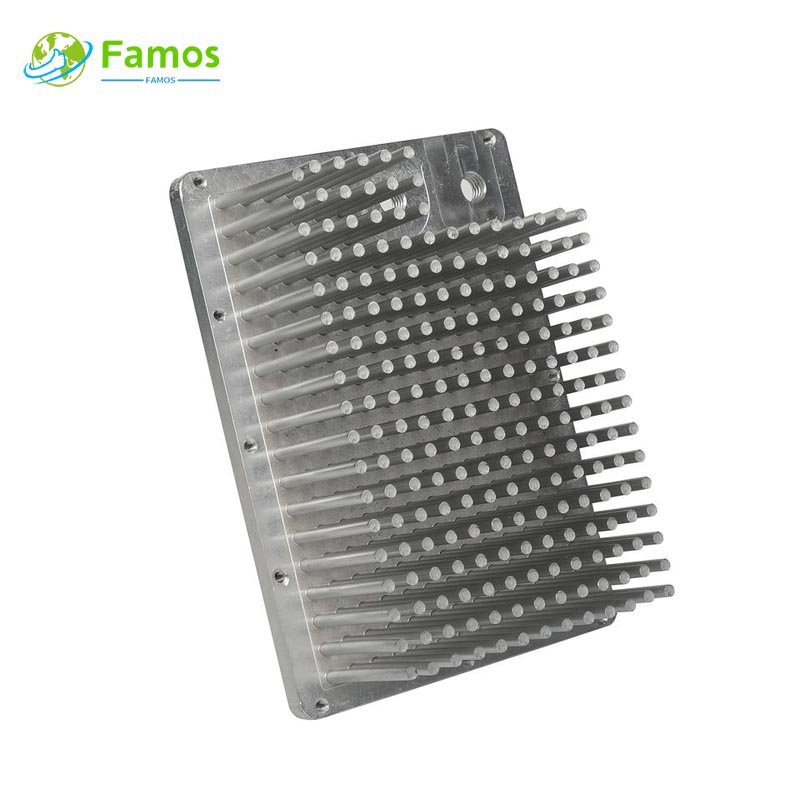
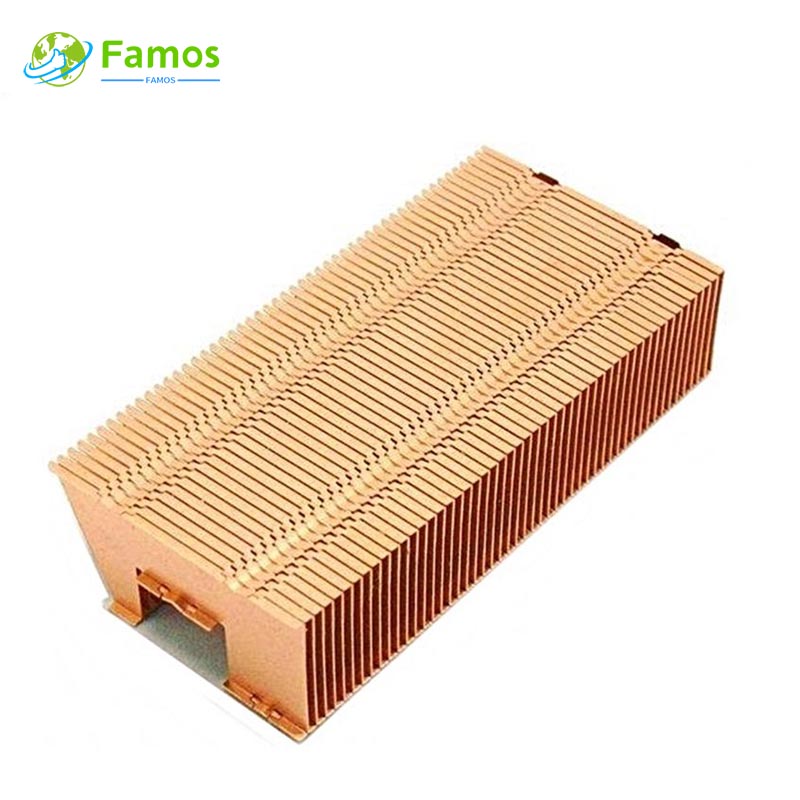
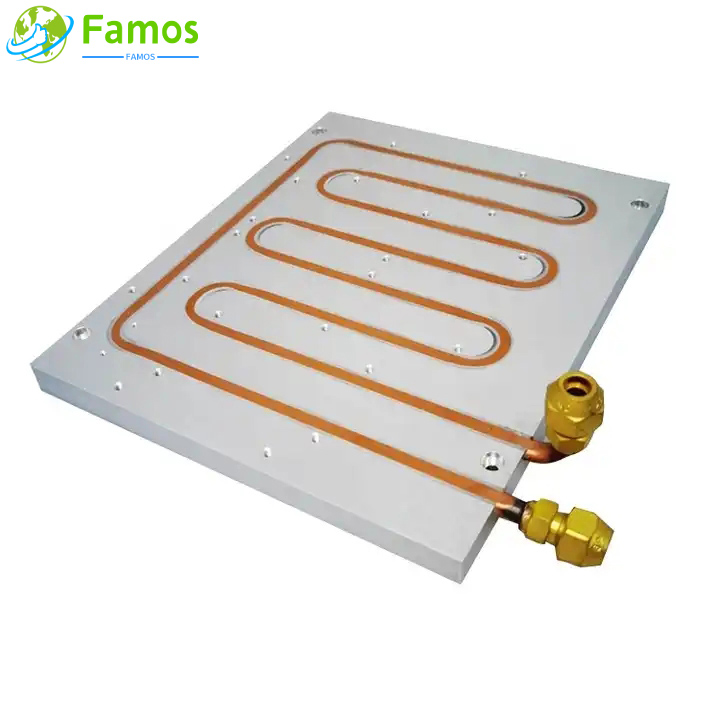
Custom heat sinks are essential components used in electronic devices to dissipate heat and regulate temperature. By dissipating heat, they prevent damage and ensure the longevity of the device. Custom heat sinks come in different shapes, sizes and materials, although their structure and fabrication process is somewhat similar.
How do you custom heat sinks? In this article, we’ll explore the process involved in designing custom heat sinks, the materials used in fabricating them, and the criteria for selecting the best custom heat sinks for your application needs.
Understanding Custom Heat Sinks
A custom heat sink is a component that serves to transfer or dissipate heat from the place where it’s generated. This includes electronic devices such as CPU, GPU, or power supply units. In a computer, the CPU serves as the primary heat source, generating heat as it processes data. Without a heat sink in place, the temperature of the device can rapidly rise and cause long-term damage.
When it comes to custom heat sinks, there is quite a bit of creativity involved in their design and manufacture. These components are typically custom-made to fit the specific application. Whether it is a computer chip, power transistor, or a motor, custom heat sinks are designed specifically to meet the unique needs of a given application.
Custom heat sinks are made from materials such as aluminum, copper, or a combination of both. Aluminum is the most common material used due to its high thermal conductivity and affordability. Copper, on the other hand, is more expensive but offers better heat transfer to air.
Structuring and Designing Custom Heat Sinks
When designing custom heat sinks, there are certain structural and design considerations that must be taken into account. The design requirements and considerations vary slightly from one application to another, depending on the application’s thermal management needs.
Many metalworking processes can be used for the production of custom heat sinks. These include extrusion, die casting, forging and stamping. Extrusion appears to be the most popular method and is the most cost-effective manufacturing method for high-volume custom heat sinks. Die casting, on the other hand, is used for high-precision custom heat sinks.
Extrusion is a popular manufacturing process that involves pushing a heated aluminum composite through a mold with a specific cross-sectional shape. The composite emerges on the other end of the mold, where it is cut to the required length. The resulting product is a heat sink with a custom profile that’s efficient in dissipating heat.
Die Casting involves pouring molten aluminum into a die mold under high pressure. The result is precision in the shape and thickness of the heat sink. In this process, additional features, such as fins, can be included in the mold. This process yields heat sinks that have high thermal conductivity and are more durable than other manufacturing methods.
For heat sinks created by either extrusion or die casting, secondary machining and finishing processes are typically applied. These processes involve drilling holes, assembling clips, and coating with a finishing coat or color.
Down below are the steps involved in custom heat sinks:
1. Selection of manufacturing process
2. Definition of geometric properties
3. Material selection
4. Size selection
5. Thermal analysis
6. Integration into the device
7. Production of prototype
8. Production optimization
Material Selection
In selecting materials for custom heat sinks, several factors are taken into consideration, including thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, mechanical properties, and cost. Aluminum and copper are the two most popular materials used, given their high thermal conductivity, light weight, and affordability.
Both aluminum and copper are classified as thermally conductive materials. Copper has a thermal conductivity rating of approximately 400W/m.K, while aluminum is approximately 230W/m.K. In addition, compared to copper, aluminum is significantly lighter and less expensive.
Size Selection
The choice of size is dependent on the specific thermal properties and the amount of heat to be dissipated and the space application can supply. Important factors include surface area and cross-sectional area. Heat dissipation is directly proportional to the surface area and inversely proportional to the thickness of the metal. Thicker metals generate less heat, while thinner metals transfer heat more efficiently.
Thermal Analysis
Thermal analysis is the study of the propagation of thermal energy within a material. Thermal simulations enable designers to determine how well a heat sink will function and how effectively it will dissipate heat. We have a comprehensive thermal simulation software that can simulate different thermal conditions to provide a better analysis of custom heat sinks.
Integration into the Device
After the heat sink design process, custom heat sinks are typically integrated into the device through various mounting methods. Some of the popular mounting options include push pins, screws, springs, or adhesives. The mounting method depends on the specific application requirements.
Production
After a successful prototype is developed, custom heat sinks are manufactured utilizing the most economical and efficient method. The final product undergoes rigorous testing to ensure the optimal performance, structural integrity, and lightness.
Conclusion
Custom heat sinks are important components of electronic devices. They help to dissipate heat, which helps to protect the device components. The process of designing and manufacturing custom heat sinks is a complex process that involves several considerations, such as material selection, size, and thermal properties. By understanding the intricacies of designing custom heat sinks, manufacturers can produce components that meet the specific design and performance requirements.
If You Are in Business, You May Like
Types of Heat Sink
In order to meet different heat dissipation requirements, our factory can produce different type heat sinks with many different process, such as below:
Post time: Jun-12-2023












