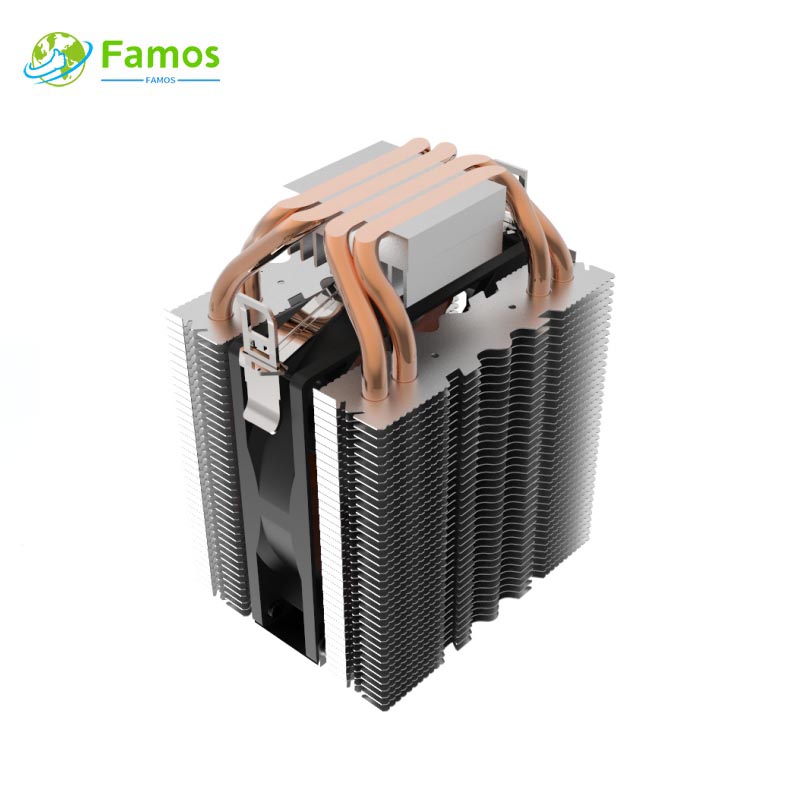
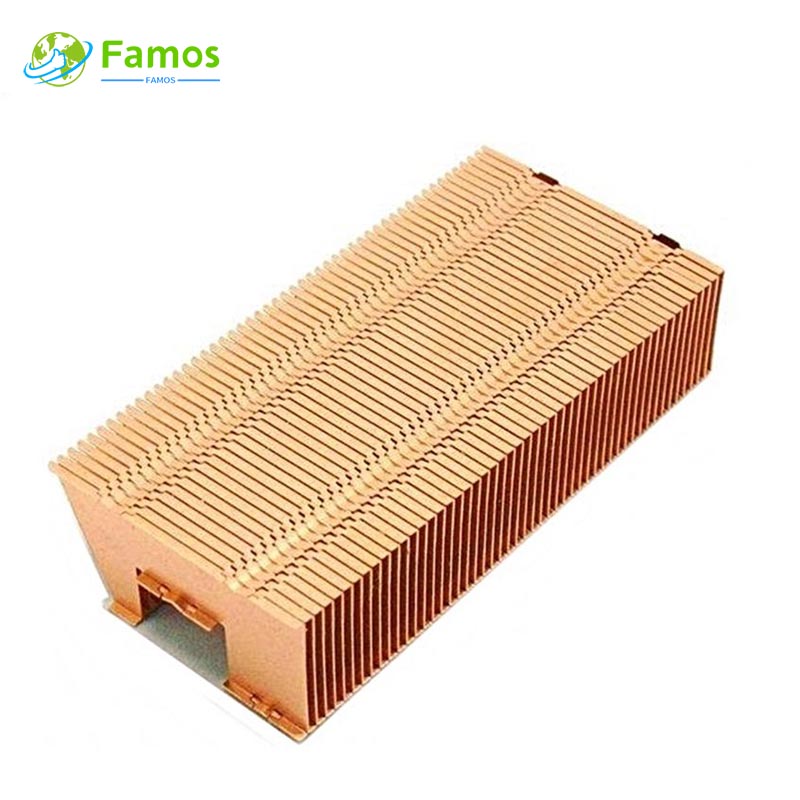
Heat sinks are vital components in electronic devices that are used to dissipate heat generated by the components. Skiving heat sinks and extrusion heat sinks are two commonly used types of heat sinks. Both types are effective at removing heat and maintaining the optimal operating temperature of electronic devices. This article aims to compare skiving heat sinks and extrusion heat sinks in terms of their design, manufacturing process, performance, and applications.
Design
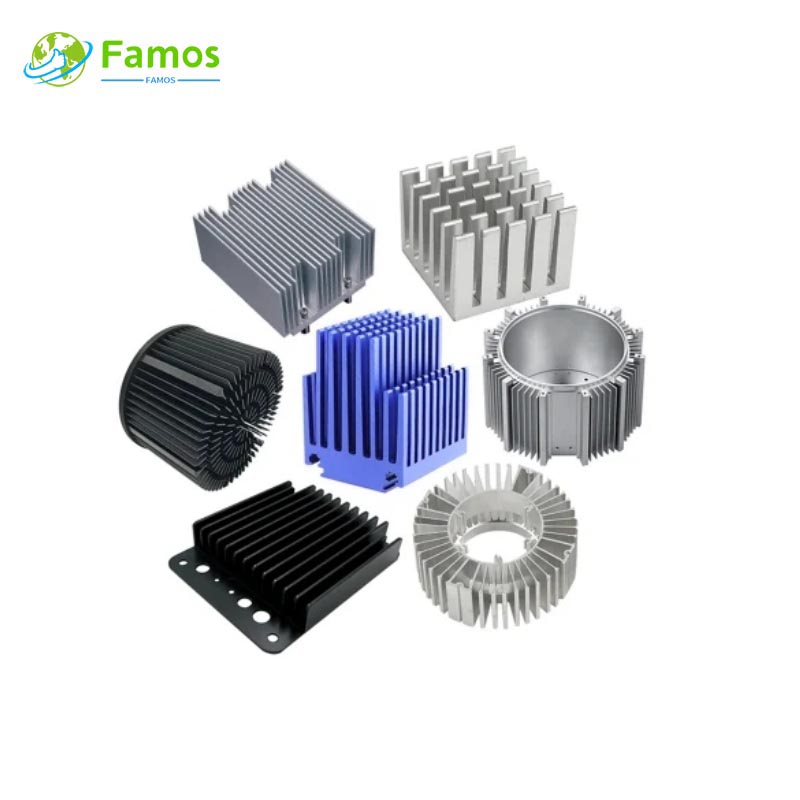
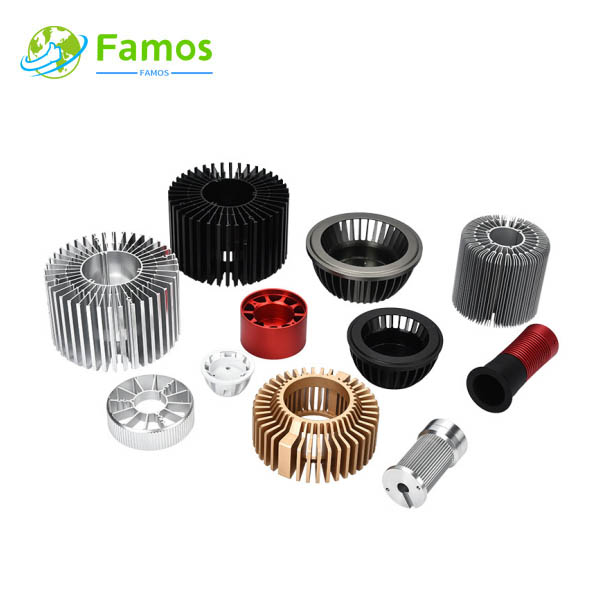
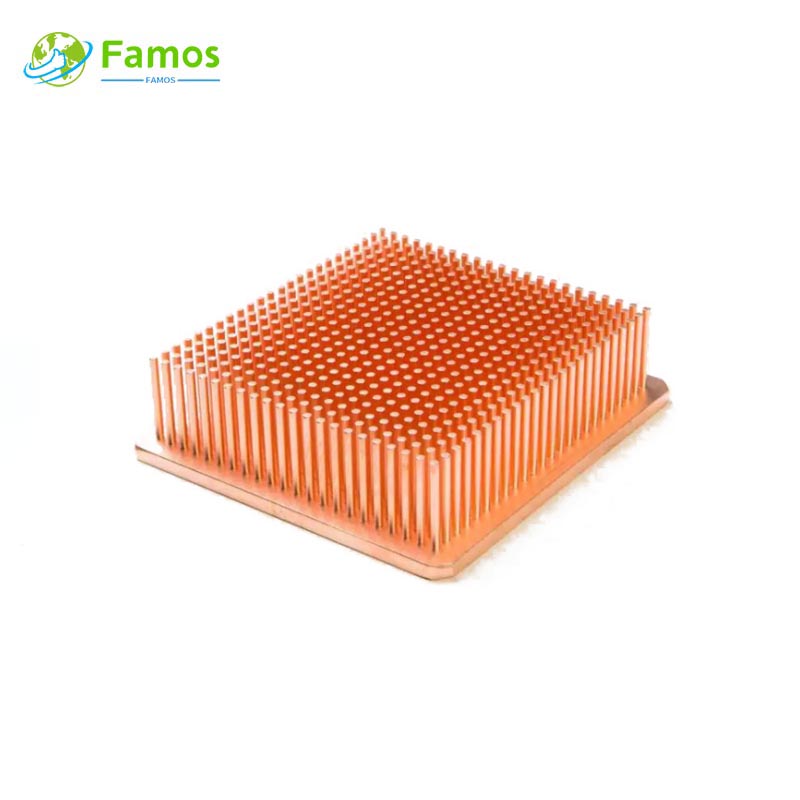
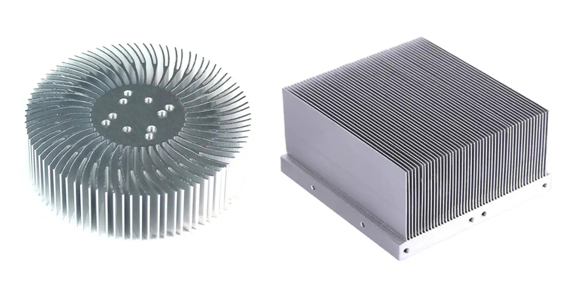
Skiving heat sinks are made from a solid block of metal, typically aluminum or copper. They consist of multiple fins that are precision machined into the block. These fins are arranged in a staggered pattern to maximize the surface area for heat transfer. The design of skiving heat sinks allows for efficient heat dissipation, especially in applications with limited space.
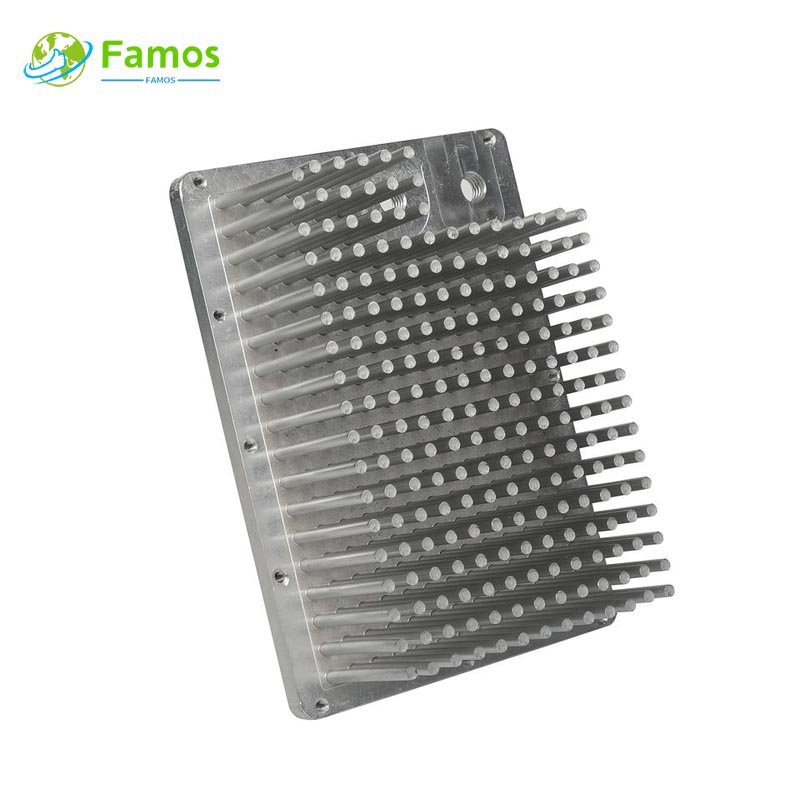
Extrusion heat sinks, on the other hand, are manufactured through an extrusion process. They are produced by pushing heated aluminum or copper through a die in the desired shape. Extrusion heat sinks can have various shapes and sizes, including flat, round, or curved. The design of extrusion heat sinks allows for high volume production and cost-effectiveness.
Manufacturing Process
Skiving heat sinks are typically manufactured using a skiving machine, which is a metalworking tool that slices thin layers of metal from a block. The skiving process involves cutting and forming the fins simultaneously. This manufacturing process is precise and can produce heat sinks with intricate fin designs. Skiving heat sinks can also be customized to meet specific cooling requirements.
The manufacturing process of extrusion heat sinks begins with the extrusion of heated aluminum or copper through a die. After extrusion, the heat sinks are stretched and cut to the desired length. Additional machining processes can be applied to create specific features, such as fins or mounting holes. The extrusion process enables the production of heat sinks in various shapes and sizes, making them highly versatile for different applications.
Performance
Both skiving heat sinks and extrusion heat sinks have excellent heat dissipation capabilities, but there are some differences in their performance. Skiving heat sinks have a higher fin density, which results in a larger surface area for heat transfer. This allows skiving heat sinks to dissipate heat more efficiently than extrusion heat sinks. Skiving heat sinks are particularly suitable for high-power applications where heat removal is crucial.
Extrusion heat sinks, on the other hand, have lower fin densities compared to skiving heat sinks. However, they can compensate for this by increasing the size of the fins or using thicker base plates. Extrusion heat sinks are more cost-effective and are widely used in applications where moderate heat dissipation is required.
Applications
Skiving heat sinks are commonly used in high-performance electronic devices, such as computer CPUs, power amplifiers, and LED lighting systems. Their efficient heat dissipation capabilities make them ideal for applications that generate a significant amount of heat.
Extrusion heat sinks have a wider range of applications due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. They are used in various electronic devices, including computer motherboards, power supplies, telecommunications equipment, and automotive electronics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both skiving heat sinks and extrusion heat sinks are effective in dissipating heat from electronic devices. Skiving heat sinks offer higher heat dissipation capabilities and are suitable for high-power applications. Extrusion heat sinks, on the other hand, are cost-effective and versatile, making them a popular choice for different applications. The selection between skiving heat sinks and extrusion heat sinks depends on the specific cooling requirements and constraints of the application.
If You Are in Business, You May Like
Types of Heat Sink
In order to meet different heat dissipation requirements, our factory can produce different type heat sinks with many different process, such as below:
Post time: Jun-30-2023